队列介绍
队列这玩意,貌似也没什么,就是一个先进先出FIFO(First Input First Output)的数据结构,主要分为顺序队列和循环队列。
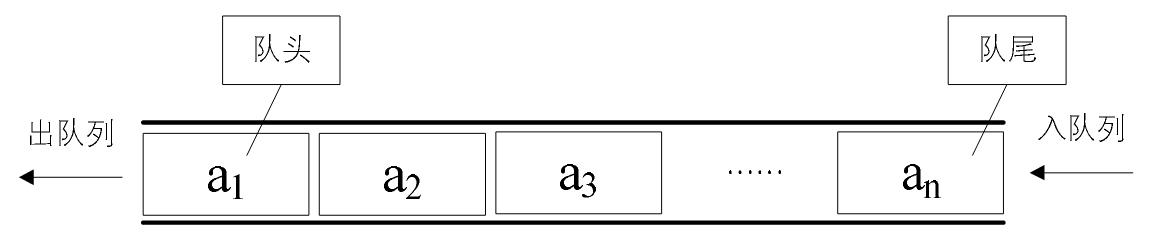
顺序队列
顺序队列在入队过程中直接在队尾插入即可,时间复杂度为O(1),而在每次出队过程都需要将所有元素向前移位,此时时间复杂度为O(n),效率低下。
循环队列
循环队列则在出队过程中不需要移动元素,而是引入两个指针front和rear分别指向队头和队尾,入队和出队只需要移动指针即可。
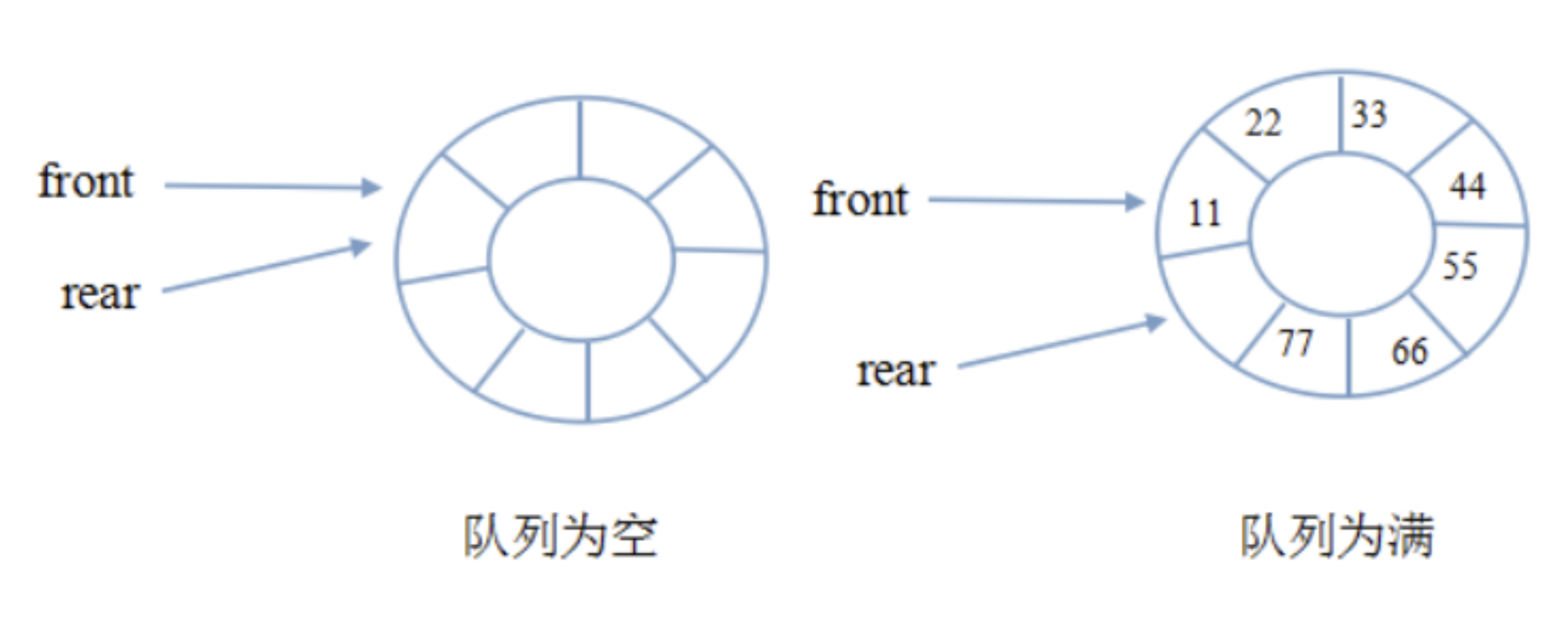
队列为空的条件:front == rear ,队列为满的条件:(rear + 1) % queue.length == front
相关操作介绍
- 元素的入队
- 元素的出队
- 返回队列的长度
- 判断队列是否为空
- 队列的生成
- 队列清空
Java实现
顺序队列
package queue;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyQueueSequence {
private Integer[] queue;
private int size = 0;
public MyQueueSequence() {
queue = new Integer[10];
}
/**
* 构造方法
*
* @param length 队列大小
*/
public MyQueueSequence(int length) {
queue = new Integer[length];
}
/**
* 入队
*
* @param value 值
*/
public void enQueue(int value) {
//若队已满抛出异常
if (size >= queue.length) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is full.");
}
queue[size] = value;
size++;
}
/**
* 出队
*
* @return 值
*/
public Integer outQueue() {
int res = queue[0];
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
queue[i] = queue[i + 1];
}
queue[size - 1] = null;
size--;
return res;
}
/**
* 获取队列长度
*
* @return 队列长度
*/
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
/**
* 检查队列是否已满
*
* @return 是否已满
*/
public boolean isFull() {
return size == queue.length;
}
/**
* 清空队列
*/
public void clear() {
size = 0;
Arrays.fill(queue, null);
}
/**
* 检查队列是否为空
*
* @return 是否为空
*/
public boolean isNull() {
return queue[0] == null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
if (isNull()) {
return "null";
}
return "MyQueueSequence{" + Arrays.toString(queue) + "}";
}
}
循环队列
package queue;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyQueue {
private Integer[] queue;
private int size = 0;
private int front = 0;//队前索引
private int rear = 0;//队尾索引
public MyQueue() {
queue = new Integer[10];
}
/**
* 构造方法
*
* @param length 队列大小
*/
public MyQueue(int length) {
queue = new Integer[length + 1];
}
/**
* 入队
*
* @param value 值
*/
public void enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is full.");
}
queue[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % queue.length;
size++;
}
/**
* 出队
*
* @return 值
*/
public Integer outQueue() {
Integer res = queue[front];
front = (front + 1) % queue.length;
size--;
return res;
}
/**
* 获取队列长度
*
* @return 队列长度
*/
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
/**
* 检查队列是否已满
*
* @return 是否已满
*/
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % queue.length == front;
}
/**
* 清空队列
*/
public void clear() {
size = 0;
front = 0;
rear = 0;
Arrays.fill(queue, null);
}
/**
* 检查队列是否为空
*
* @return 是否为空
*/
public boolean isNull() {
return front == rear;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
if (isNull()) {
return "null";
}
int i = front;
String str = "";
while (i != rear) {
str += queue[i] + ",";
i = (i + 1) % queue.length;
}
str = str.substring(0, str.length() - 1);
return "MyQueueSequence{" + str + "}";
}
}
测试类
package queue;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueueSequence myQueueSequence = new MyQueueSequence(5);
myQueueSequence.enQueue(1);
myQueueSequence.enQueue(2);
myQueueSequence.enQueue(3);
myQueueSequence.enQueue(4);
myQueueSequence.enQueue(5);
System.out.println(myQueueSequence);
System.out.println(myQueueSequence.isFull());
System.out.println(myQueueSequence.getSize());
System.out.println(myQueueSequence.outQueue());
System.out.println(myQueueSequence);
System.out.println(myQueueSequence.outQueue());
System.out.println(myQueueSequence.outQueue());
System.out.println(myQueueSequence.getSize());
myQueueSequence.enQueue(6);
System.out.println(myQueueSequence);
System.out.println(myQueueSequence.isNull());
myQueueSequence.clear();
System.out.println(myQueueSequence.isNull());
System.out.println(myQueueSequence);
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue(5);
myQueue.enQueue(1);
myQueue.enQueue(2);
myQueue.enQueue(3);
myQueue.enQueue(4);
myQueue.enQueue(5);
System.out.println(myQueue);
System.out.println(myQueue.isFull());
System.out.println(myQueue.getSize());
System.out.println(myQueue.outQueue());
System.out.println(myQueue);
System.out.println(myQueue.outQueue());
System.out.println(myQueue.outQueue());
System.out.println(myQueue.getSize());
myQueue.enQueue(6);
System.out.println(myQueue);
System.out.println(myQueue.isNull());
myQueue.clear();
System.out.println(myQueue.isNull());
System.out.println(myQueue);
}
}
